Futures vs. Options
Futures and options are types of contracts that allow investors to trade underlying assets at specific prices. Both of these contracts are sold in exchanges, so they are financial products. Investors use these products to turn a profit or to hedge current investments. Both futures and options come with unlimited potential for profit, but the potential for profit loss with futures could be greater.
If you are considering buying a futures or options contract, you need to learn about the differences between these contracts. You also need to consider the advantages of futures over options contracts, as well as the disadvantages of buying futures.
Here are the key takeaways:
- Both types of contracts are connected to specific dates.
- The counterparties are only obligated to act on one futures contract.
- An option contract gives investors the right, as opposed to the obligation, to buy and sell shares at a specific price at any time during the life of the contract. An option buyer could even sell the option at any time before the expiration date.
- Options contracts could have futures as their underlying assets.
- Futures contracts have unlimited risk, but the risk for long options is limited.
- The time value of money is crucial to an options contract.
What are Futures and Options?
A futures contract is an agreement in which two parties will trade an underlying asset at a future date and at a predetermined price. The buyer is obligated to buy the asset and the seller is obligated to sell it. Buyers must pay fees in futures trading, which includes commissions on the trade.
An options contract gives investors the right, as opposed to the obligation, to buy and sell shares at a specific price at any time during the life of the contract. There is an expiration date connected to the option, so the buyer must decide to buy an asset any time during the life of the contract. In options trading, buyers must also pay a premium or buy the contract at a discount that the seller offers. However, these fees are never fixed, and they are determined by the volatility of the financial product and the volatility of the market.
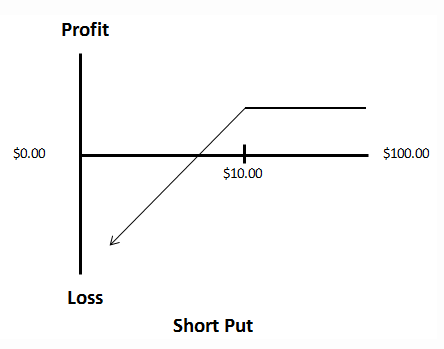
There are two types of options: calls and puts. A call option is an offer to buy a stock at the strike price before the expiration date. A put option is an offer to sell a stock at a set price before the expiration date.
Futures Options Contracts
In some cases, the underlying asset of an options contract is a futures contract. When someone buys this option, they may choose whether to buy the futures contract before a specific date. If the futures options buyer exercises their option, they will assume the position of the seller as the holder of the futures contract.
Trading Futures vs. Options
Futures and options have a few similarities:
- Options and futures are financial products.
- These contracts are traded on exchanges.
- Both a futures contract and an options contract are standardized.
- Futures and options are applied to margin accounts.
- Both categories of contracts have daily settlements.
- These contracts are governed by underlying assets such as currencies, stocks, bonds, and other financial products.
Here are the key differences between futures and options:
- A futures contract binds the counterparties to buy and sell a financial product on a specific date and at a specific price. An options contract allows investors to buy and sell a financial product before the expiration date; neither party is bound to exercise that right.
- The buyer does not need to pay anything upfront to secure a futures contract beyond commission. Buyers who secure options contracts must make premium payments.
- Unlike with futures contracts, options contracts allow buyers and sellers to exercise their rights any time before the expiration date.
- With futures contracts, there are no limits placed on the profits or losses investors can receive. Long options contracts create significant profit potential, but cap losses.
- The time value of money is crucial to whether an options contract will be executed. This is not a concern with a futures contract since its execution is guaranteed.
- The fees associated with futures trading generally remain constant, but the fees connected to options trading are volatile.
Advantages of Futures Contracts vs. Options Contracts
Futures contracts have a few outstanding advantages over options contracts:
- Futures give more investors access to certain markets. Futures markets were originally meant for commodities traders, but they are now open to investors and speculators who don’t want to take physical possession of commodities.
- Futures have fixed trading costs. The margin requirements for many commodity and currency futures are relatively stable from year to year, so traders generally know how much they will pay upfront. By comparison, option premiums can vary due to the volatility of an underlying asset or market.
- Futures can protect investors from price fluctuations. In a matter of months to a year, the costs of producing certain commodities can rise or fall, and so could the bids for those commodities. By purchasing a futures contract, a seller could lock in an acceptable price to sell those commodities at a future date.
- Futures contracts have no time decay. Options are known as wasting assets because their value declines over time. By comparison, futures contracts have a set value.
- Futures markets have high liquidity. Since there are many investors in certain futures markets, the flow of money is high. There are narrower bid-ask spreads and traders can enter or exit their positions when they need to.
- The pricing of futures contracts is easier to understand. Investors know that they will have to pay fees like commissions on trade, fees to the exchange and broker, and any expenses tied to margin calls. These fees generally remain constant.
Disadvantages of Futures Contracts
- Futures contracts are susceptible to uncontrollable events. Certain events can remove the profitability of an investment, even if the price for a sale is locked in. For example, crops are especially vulnerable to changes in weather or natural disasters.
- There are leverage issues connected to futures contracts. While leverage can be an advantage (a trader can buy a futures contract for a fraction of its value) and the daily increases in futures are reflected in that trader’s margin account, daily price changes can negatively impact margin accounts. Sometimes, the quick drop in futures prices may cause investors to put more money in their accounts to meet minimum requirements.
- Futures contracts are complex. Although the pricing for these contracts is relatively simple, the terms of the contracts themselves are complex, as are all related variables that can affect the prices of futures, like weather, political upheaval, and changing financial conditions.
- The potential for profit could decrease over time. Even though futures contracts are not subject to time decay, the profitability of futures could still suffer over time as investors lose interest or confidence in certain underlying assets.
When Should You Purchase a Futures or Options Contract?
Here are a few scenarios when you should consider buying a futures or options contract.
- Futures contracts are well suited for investing in commodities, currencies, and indexes. Investors who purchase these contracts want to lock in certain prices before they rise, while sellers are hedging against price drops.
- Investors and speculators who want to profit from price changes can purchase futures contracts, then sell them before the expiration date. They do not want to take actual possession of the underlying assets.
- Options contracts are better suited for speculating on stocks.
As you can see, there are vast differences between options and futures contracts. Although futures have more advantages and options are volatile, there are great risks associated with both types of contracts, and futures can have a greater risk in certain situations.