1.0 Beginner: The Basics of Options
- What is an option?
- A financial tool called a derivative
- A financial tool to trade future contracts
- A financial tool to trade foreign exchange
- A financial tool called a LEAP
Answer: A
Notes:
- Options are financial tools that are called derivatives.
- Derivatives are based on the value of underlying securities, such as stocks.
- What is an option contract?
- Gives an investor the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a stock at an agreed upon price.
- Gives an investor the obligation to buy or sell a stock at an agreed upon price.
- Gives an investor the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a stock at any price.
- Gives an investor the obligation to buy or sell a stock at any price.
Answer: A
Notes: A stock option gives an investor the right, but not the obligation, to buy or sell a stock at an agreed upon price.
- What is a call option?
- Call options offer the writer the opportunity to buy the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Call options offer the writer the opportunity to sell the underlying asset at the current market price.
- Call options offer the buyer the opportunity to buy the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Call options offers the buyer the opportunity to sell the underlying asset at the current market price.
Answer : C
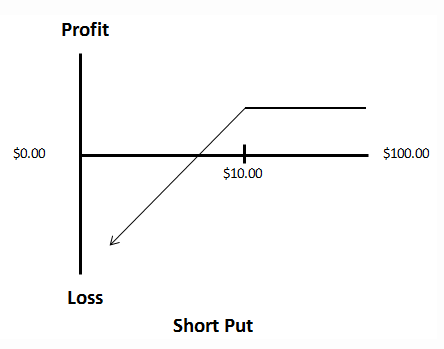
- What is a put option?
- Put options offer the writer the opportunity to sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Put options offer the buyer the opportunity to sell the underlying asset at the strike price.
- Put options offer the buyer the opportunity to buy the underlying asset at the current market price..
- Put options offer the writer the opportunity to buy the underlying asset at the current market price.
Answer: B
- What are weekly contracts?
- Options contracts that expire on every second Friday of the month.
- Options contracts that expire on every third Thursday of the month.
- Options contracts that expire on Friday of every week.
- Options contracts that expire on Saturday of every week.
Answer : C
- What are standard monthly contracts?
- Options contracts that are issued with 9 month expirations and expire on the Saturday following the 3rd Friday of every month at 11:59pm EST.
- Options contracts that are issued with 12 month expirations and expire on the Sunday following the 2nd Friday of every month at 11:50pm EST.
- Options contracts that are issued with 6 month expirations and expire on the Friday following the 2nd Friday of every month at 11:59 EST.
- Options contracts that are issued with 9 months of expiration and expire on the Saturday of the 2nd Friday of every month at 11:59pm EST.
Answer: A
- What does the OCC stand for?
- Options Clearing Company
- Options Clearing Committee
- Options Conference Committee
- Options Concile Company
Answer : B
- What are Listed Stock Options?
- Listed Options are futures options that are a put or call that is traded on a national options exchange, and have a fixed strike price and a fixed expiration date.
- Listed Options are a put or call that is traded on a national options exchange, and have variable strike prices and fixed expiration dates
- Listed Options are a put or call that is traded on a regional options exchange only, and have variable strike prices and variable expiration dates.
- Listen Options are a put or call that is traded on a national options exchange, and have a fixed strike price and a fixed expiration date.
Answer : D
- What is the underlying security for stock options?
- The stock that can be purchased or sold upon exercise of options contracts
- The future that can be purchased or sold upon exercise of options contracts
- The stock that can be purchased or sold without exercise of options contracts
- The future that can be purchased or sold without exercise of options contracts
Answer : A
- What does it mean to exercise an option?
- To implement the right for the option holder to buy (for a call) or sell (for a put) the underlying security at the market price.
- To implement the right for the option holder to sell (for a call) or buy (for a put) the underlying security at the listed strike price.
- To implement the right for the option seller to sell (for a call) or buy (for a put) the underlying security at the listed strike price.
- To implement the right for the option holder to buy (for a call) or sell (for a put) the underlying security at the listed strike price.
Answer : D
Notes:
- Options are typically exercised when they are in the money.
- When do listed equity options settle?
- Settle “non-regular way”, or two business days from the expiration date
- Settle “regular way”, or four business days from the expiration date
- Settle “regular way”, or three business days from the expiration date
- Settle “non-regular way”, or four business days from the expiration date
Answer : C
- What is the strike price of an option?
- The price at which the holder of an option can buy (for a call) or sell (for a put) the underlying security when the option is exercised.
- The price at which the seller of an option can sell (for a call) or buy (for a put) the underlying security when the option is exercised.
- The price at which the holder of an option can buy (for a call) or sell (for a put) the underlying security before the option is exercised.
- The price at which the seller of an option can buy (for a call) or sell (for a put) the underlying security before the option is exercised.
Answer : A
- How is options premium calculated?
- Option Premium = Intrinsic Value + Extrinsic Value
- Option Premium = Intrinsic Value – Extrinsic Value
- Option Premium = Intrinsic Value + Extrinsic Value + Strike Price
- Option Premium = Intrinsic Value – Extrinsic Value + Strike Price
Answer : A
- How is Intrinsic Value calculated?
- Difference between the strike price and market price of the underlying security.
- Difference between the market price and the current option price
- Difference between the current option price and At-the-Money (ATM) option price
- Difference between the At-The-Money (ATM) option price and the market price of the underlying security
Answer: A
Notes: Intrinsic Value = Strike Price – Market Price of security
- How is Extrinsic Value calculated?
- The sum of the strike price of an option and the intrinsic price minus the market price, also known as its premium.
- The difference between the market price of an option, also known as its premium, and its intrinsic price.
- The difference between the market price of an option, also known as its premium, and its strike price.
- The difference between the strike price of an option and the intrinsic price plus premium
Answer: B
Notes:
- Extrinsic Value = premium – intrinsic price
- Extrinsic Value is also known as time value
- What are the types of options?
- Calls and Puts
- Strikes and Market price
- Calls only
- Puts only
Answer : A
- What is an options class?
- Every Call or every Put of an underlying stock, regardless of expiration month and strike price.
- Every Call or every Put of an underlying stock, in the same expiration month and same strike price.
- Every Call of an underlying stock, regardless of expiration month and strike price.
- Every Put of an underlying stock, regardless of expiration month and strike price.
Answer : A
- What is an option expiration?
- The day after the final date on which the derivatives contract is valid
- The final date on which the derivatives contract is valid
- The day prior the final date on which the derivatives contract is valid
- Two days prior the final date on which the derivatives contract is valid
Answer : B
Notes:
- All contracts have a specified life cycle and expire on a specific date.
- What does Out of the Money (OTM) of a call refer to?
- call is “Out-of-the-Money” (OTM) when the market price is higher than strike price.
- A call is “Out-of-the-Money” (OTM) when it has only intrinsic value and no extrinsic value.
- A call is “Out-of-the-Money” (OTM) when the market price is equal to the strike price.
- A call is “Out-of-the-Money” (OTM) when the market price is lower than strike price.
Answer : D
- What does Out-of-the-Money (OTM) of a put refer to?
- A put is “Out-of-the-Money” (OTM) when it has only intrinsic value and no extrinsic value.
- A put is “Out-of-the-Money” (OTM) when the market price is equal to the strike price.
- A put is “Out-of-the-Money” (OTM) when the market price is higher than the strike price.
- A put is “Out-of-the-Money” (OTM) when the market price is lower than the strike price.
Answer : C
- What does In The Money (ITM) of a call refer to?
- A call is “in the money” when the market price is lower than the strike price.
- A call is “in the money” when the market price is higher than the strike price.
- A call is “in the money” when the market price is equal to the strike price.
- A call is “in the money” when the option possesses extrinsic value and no intrinsic value.
Answer : B
Notes:
- A call option is in the money (ITM) if the market price is above the strike price.
- ITM options only possess intrinsic value, and no extrinsic value
- What does In The Money (ITM) of a put refer to?
- A put is “in the money” when the market price is lower than the strike price.
- A put is “in the money” when the market price is higher than the strike price.
- A put is “in the money” when the market price is equal to the strike price.
- A put is “in the money” when the option possesses extrinsic value and no intrinsic value.
Answer : A
Notes:
- A put option is in the money if the market price is below the strike price.
- ITM options only possess intrinsic value, and no extrinsic value
- What does At The Money (ATM) refer to?
- When an option’s strike price is less than the market price of the underlying security.
- When an option’s strike price is greater than the market price of the underlying security.
- When an option’s strike price is equal to the market price of the underlying security.
- When the market price of the underlying security is equal to the option’s strike price plus breakeven price
Answer : C
- How do you calculate the breakeven price of a long call?
- Breakeven = Strike Price + Market Price
- Breakeven = Cost – Strike Price
- Breakeven = Cost + Strike Price
- Breakeven = Strike Price – Market Price
Answer : C
- How do you calculate the breakeven price of a long put?
- Breakeven = Strike Price + Market Price
- Breakeven = Cost – Strike Price
- Breakeven = Cost + Strike Price
- Breakeven = Strike Price – Market Price
Answer : B
- How do you calculate the breakeven price of a covered call?
- Breakeven = call option premium – market price of stock at initiation
- Breakeven = call option premium + market price of stock at initiation
- Breakeven = call option premium – current market price
- Breakeven = call option premium – strike price
Answer : A
- How do you calculate the breakeven price of a protective put?
- Breakeven = current price of stock – premium paid
- Breakeven = purchase price of stock – premium paid
- Breakeven = current price of stock + premium paid
- Breakeven = purchase price of stock + premium paid
Answer : D
- What are the 4 factors that impact options premium?
- implied volatility, intrinsic value, time remaining until expiration
- historical volatility, intrinsic value, time remaining until expiration
- implied volatility, intrinsic value, time remaining until expiration, interest rates
- historical volatility, extrinsic value, time remaining until expiration, interest rates
Answer : C
- What is Implied Volatility?
- IV is a metric that captures the market’s view of the likelihood of changes in a given security’s price
- IV is a metric that captures the market’s view of the likelihood of a change in a given security’s delta
- IV is a metric that captures the market’s view of the likelihood of a change in a given security’s time value
- IV is a metric that captures the market’s view of the likelihood of a change in a given security’s historical volatility
Answer : A
- What are the 5 common options greeks?
- Delta, Gamma, Theta, Vega, Rho
- Vomma, Volta, Surge, Speed, Delta
- Delta, Theta, Rho, Volga, Vomma
- Gamma, Delta, Vola, Volga, Theta
Answer : A
Notes: Option greeks us a term used to describe the different dimensions of risk involved in taking an options position
- What does the greek, Delta, represent?
- Represents the rate of change between the options price and $4 change in the underlying asset’s price.
- Represents the rate of change between the theta and $3 change in the underlying asset’s price.
- Represents the rate of change between the gamma and $2 change in the underlying asset’s price.
- Represents the rate of change between the options price and $1 change in the underlying asset’s price.
Answer : D
Notes: Calls have a positive delta, between 0 and 1. Puts have a negative delta, between 0 and -1
- What does the greek, Gamma, represent?
- Represents the rate of change between the options theta and the underlying asset price.
- Represents the rate of change between the options delta and the underlying asset price
- Represents the rate of change between the options vega and the underlying asset price.
- Represents the rate of change between the options rho and the underlying asset price.
Answer : B
Notes:
- Second order derivative
- Indicates the amount the delta would change given a $1 move in underlying asset’s price
- What does the greek, Theta, represent?
- Represents the rate of change between the options price and historical volatility, or options volatility sensitivity
- Represents the rate of change between the options implied volatility and time, or options vomma sensitivity
- Represents the rate of change between the options price and time, or options time sensitivity
- Represents the rate of change between the options price and delta, or options dollar sensitivity
Answer : C
Notes:
- Also known as option’s time decay
- Theta increases when options are At the money
- Theta decreases when options are In the money or Out-of-the-money
- As options near expiration, Theta will increase significantly
- What does the greek, Vega, represent?
- Represents the rate of change between the underlying market price and implied volatility.
- Represents the rate of change between an option’s value and the underlying assets implied volatility.
- Represents the rate of change between the option’s delta and the underlying assets implied volatility.
- Represents the rate of change between the option’s time value theta and the underlying assets implied volatility.
Answer : B
Notes:
- Known as the option’s sensitivity to volatility
- Vega indicates the amount the options price will change given a 1% change in implied volatility
- What does the greek, Rho, represent?
- Represents the rate of change between an option’s value and a 2% change in market price.
- Represents the rate of change between an option’s value and a 3% change in delta.
- Represents the rate of change between an option’s value and a 4% change in volatility.
- Represents the rate of change between an option’s value and a 1% change in interest rates.
Answer : D
Notes:
- This measures the sensitivity to interest rates.
- When are Weekly options contracts issued?
- Issued Wednesday and expire the following Thursday
- Issued Tuesday and expire the following Wednesday
- Issued Friday and expire the following Thursday
- Issued Thursday and expire the following Friday
Answer : D